What is an Aerosol?
Scientifically, an aerosol is a dispersion of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas.
Daily Examples:
- Fog:Liquid droplets in ai
- Smoke:Solid particles in air
- Air pollution:Solid particles in air
Typically, particle size would be less than 5 microns
In our industry, we define an aerosol as a sealed, ready to use pressurised package which will dispense a product on actuation of the valve.
Article 2 of ADD* defines an ‘aerosol dispenser’ as “any non reusable container made of metal, glass or plastic and containing a gas compressed, liquified or dissolved under pressure, with or without a liquid, paste or powder, and fitted with a release device allowing the contents to be ejected as solid or liquid particles in a suspension in a gas, as a foam, paste or powder, or in a liquid state.”
*ADD: EU Aerosol Dispensing Directive
What is an Aerosol?
Scientifically, an aerosol is a dispersion of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas.
Daily Examples:
- Fog:Liquid droplets in ai
- Smoke:Solid particles in air
- Air pollution:Solid particles in air
Typically, particle size would be less than 5 microns
In our industry, we define an aerosol as a sealed, ready to use pressurised package which will dispense a product on actuation of the valve.
Article 2 of ADD* defines an ‘aerosol dispenser’ as “any non reusable container made of metal, glass or plastic and containing a gas compressed, liquified or dissolved under pressure, with or without a liquid, paste or powder, and fitted with a release device allowing the contents to be ejected as solid or liquid particles in a suspension in a gas, as a foam, paste or powder, or in a liquid state.”
*ADD: EU Aerosol Dispensing Directive
Key Components
Working Principle
Working Principle
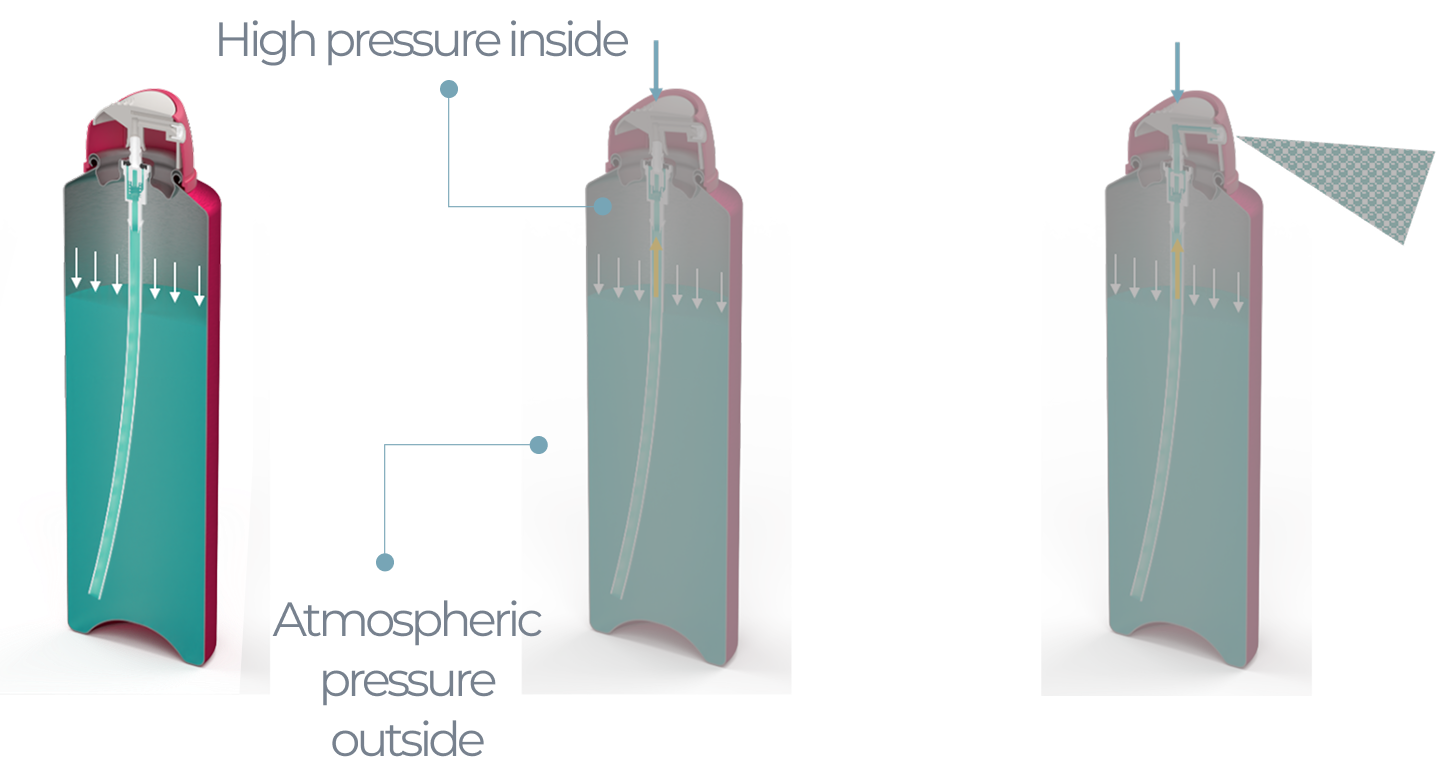
An aerosol is a pressurised package
The pressure inside the container is higher than the atmospheric pressure outside the container
A propellant (liquified or compressed gas of some type) exerts pressure onto the product inside the container
When the valve is opened the pressure pushes the product up the diptube into the valve and through the actuator to dispense the product.
Whether the product is dispensed as a spray, foam or gel will depend on the combination of the formulation, propellant, valve and actuator type used
Working Principle
Working Principle
An aerosol is a pressurised package
The pressure inside the container is higher than the atmospheric pressure outside the container
A propellant (liquified or compressed gas of some type) exerts pressure onto the product inside the container
When the valve is opened the pressure pushes the product up the diptube into the valve and through the actuator to dispense the product.
Whether the product is dispensed as a spray, foam or gel will depend on the combination of the formulation, propellant, valve and actuator type used
Liquified Propellant Gas (LPG)
DiscoverCompressed
Gasses
DiscoverLiquified Propellant Gas (LPG)
Discover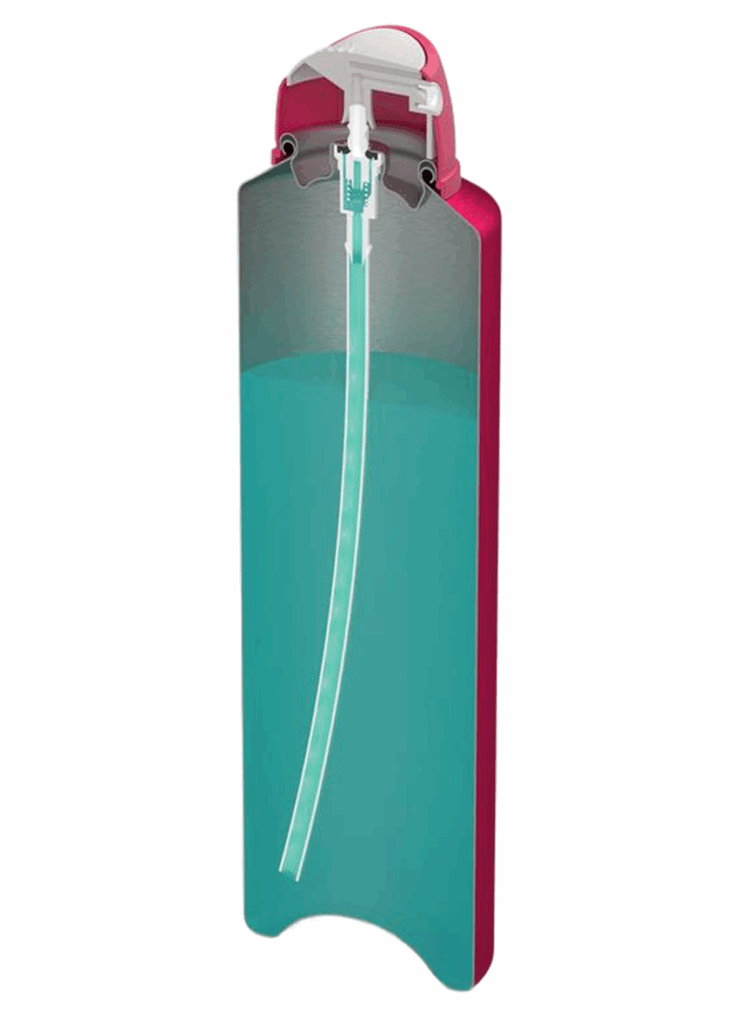
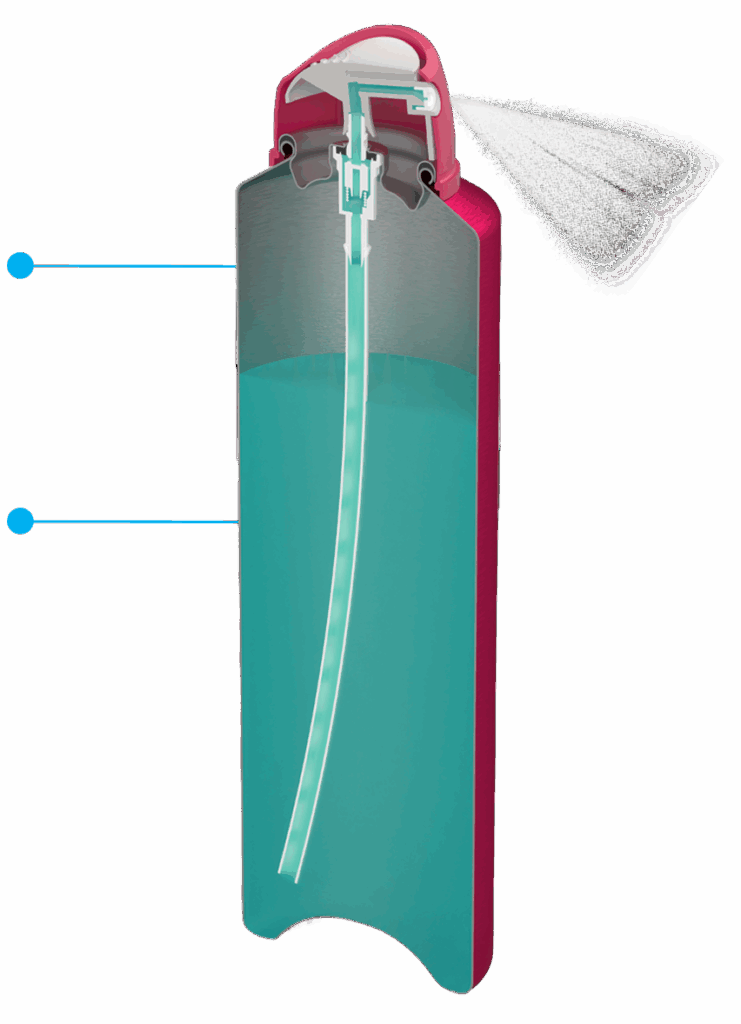
Gas-phase propellant applying pressure
Product concentrate, solvent, and liquefied propellant, possibly in two phases
The spray contains propellant and forms via liquefied gas vaporization and mechanical breakup by the valve and actuator
Constant Pressure:
Final can pressure remains the same as the initial liquefied gas is a gas or vapour cooled below its boiling point.Effective Range:
Suitable as an aerosol propellant if vapour pressure is between 2.0 and 4.7 bar.Compressed gas propellant applying pressure
Product concentrate, and solvent
The spray contains no propellant and relies entirely on the mechanical breakup provided by the valve and actuator
Initial pressure:
Typically up to 10 bar.Final pressure:
Ranges from 1 to 3 bar, depending on the solubility of the propellant in the product solution.Regulatory update:
Recent changes to the ADD allow pressures up to 15 bar at 50°C for compressed gases